The woman`s ovaries take care of some vital body functions, from housing the cells of the eggs which allow the woman to have a baby to regulating the levels of her hormones.
If the doctor tells you that either one or both your ovaries are enlarged, it is quite understandable if you become rather anxious.
What Are Ovaries?
Ovaries are the reproductive organ of the female, which produces eggs and hormones like progesterone, estrogen or androgen. When because of a certain reason, the ovary increase in size over its normal limits, then the medical condition is known as enlarged ovaries.
This particular condition occurs in either one of the ovaries or both. In certain women, increased ovaries don`t show any symptoms, but in most cases, this condition brings pain with it and might affect the daily activities of the person involved.
Symptoms of Increased Ovaries
- Dysuria.
- Occasional missed periods.
- Urgent need for urination.
- Breast pain.
- Loss of appetite.
- Gaining weight without an intention.
- Lower back or abdominal pain.
- Menorrhagia.
- Sexual contact associated with pain.
- Vaginal bleeding.
- Nausea.
- Body aches.
- Constipation.
What Causes Enlarged Ovaries?
Corpus Luteum Cyst
Usually, after the woman`s egg gets released from its follicle, the follicle turns into a secretory gland known as corpus luteum. This gland produces high amounts of progesterone and estrogen in preparation for birth.
Typically, if there`ll be no conception, this gland fills with blood or fluid, and turns into a cyst, remaining in one of the ovaries. This kind of cyst might break around the menstruation time, and then might disappear completely.
Ovarian Cancer
Lots of distinct kinds of ovarian cancer and they all have different degrees of malignancy. Depending on the type of cancer, it may be a probable reason of increased ovaries.
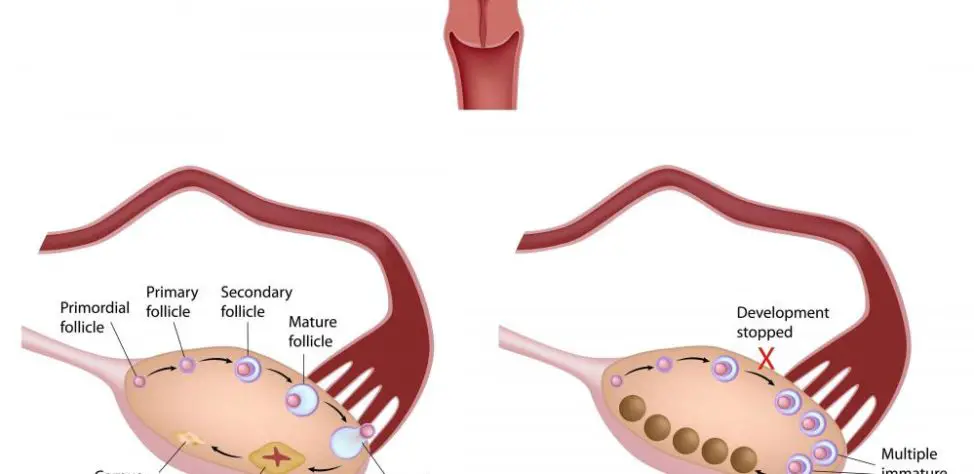
Ovulation
As you may already know, ovulation is that particular part of the woman`s cycle when her ovary will release an egg. It occurs at around day 14 of the menstrual cycle.
Just before the woman ovulates, the follicles in her ovaries increase as her eggs develop and prepare to be released.
Other ovulation symptoms will include:
- Mild cramping.
- A change or increase in vaginal discharge.
- A mild body temperature increase.
Metastatic Cancer
The most dangerous cancer form is metastatic, meaning it may spread to other different organs. Lung, peritoneum or liver cancer might be metastasizing to the woman`s ovaries.
Follicle Cyst
Follicle cyst is the most frequently encountered type of ovarian cyst. In typical conditions, graafian follicle will burst around mid-cycle and releases one or more eggs. However, if for some reason the follicle does not break or release the egg and it grows, then it could turn into a follicle cyst.
PCOS
A series of signs which occur because of the increased male hormones (androgens) in the body of the woman, leading to an imbalance of hormones. It includes signs like increased hair on the face or body, pelvic discomfort, lack of menstruation, a patch of dark skin, and acne.
The reasons for them occurring come from a mixture of genetic and environmental factors, although the precise reason for its occurrence isn`t yet completely understood.
Dermoid Cyst
These cysts contain components or tissues and organs and are frequently known as a type of cystic teratoma. Their contents are things such as sweat glands, teeth, skin, bones, hair, eyes, cartilage and nails. This kind of cysts has a tendency of being present at birth, and don`t become noticeable until later in life.
Ovarian Torsion
This occurs when the woman`s ovary and a portion of the uterine tube will twist around. It frequently occurs due to a cyst or other type of growth on one of the ovaries. At times, ovaries twist as they are a lot more flexible than a normal ovary.
Ovarian torsion is more prone to affect women during their years of reproduction.
Signs of ovarian torsion may include:
- Vomiting.
- Lower abdominal or pelvic discomfort, which can either be continuous or it can come and go.
- Nausea.
Management & Treatments
The treatment of increased ovaries generally depends on the swelling cause.
Benign Growths
This type of growths do not spread and cause danger to other tissues. However, they may still lead to medical issues if they increase in size too much and make the ovaries to twist. The doctor might advise you to remove them by surgery.
Related: How To Get Rid Of Montgomery Glands?
Functional Cysts
Cysts which are the result of the cycle`s normal processes are known as functional cysts. In lots of situations, this kind of cysts will eventually go away by themselves, and do not require any particular treatment.
Still. If you experience such cysts often, the doctor might recommend some oral contraceptives to aid stabilize the levels of your hormones. This won`t shrink your cysts, but might aid prevent any new cysts from increasing in size.
Malignant Growths (Ovarian Cancer)
If found early, these growths can be treated. Still, in a lot of situations, they aren`t found until signs start to appear and the cancer is already pretty advanced.
If you experience such a growth, the doctor will recommend surgery to remove the cancer, or perhaps the whole ovary that was affected. If your cancer may have spread, this might mean you`ll have your uterus and fallopian tubes removed as well. Your doctor might also prescribe some chemotherapy to get rid of any dangerous cells remained from the cancer.
When to Get in Touch with the Doctor?
If you feel something is wrong, you should see a doctor for a pelvic examination that could show if one of your ovaries is increased in size. However, it won`t tell the doctor what is the cause. You could then perform a blood test or transvaginal ultrasound to help your gynecologist find out whether is ovarian cancer or not.
If the examinations will show that your growth is cancerous, the doctor will probably make a biopsy on the ovary involved. Generally, this is performed through a laparoscopy, or on occasion, through laparotomy. – Visit this page!
You should also contact you healthcare provider if you start having:
- Discomfort during sexual contact.
- Skipped menstruations.
- Abnormal vaginal discharge.
- Abdominal fullness or discomfort.
- Excessive bleeding.
You should report any signs that may worry you to your gynecologist, especially if you don`t know what could be the reason for them.
The post What Can Cause An Enlarged Ovary? first appeared on PregWorld.